|
Dew Stats for .NET
|
|
Dew Stats for .NET
|
Triple exponential smoothing.
|
Parameters |
Description |
|
[In] TVec Y |
Time series data set. |
|
[In] TVec S |
Smoothed values (see above equation). Size and complex properties of S are set automatically. |
|
[In] TVec B |
Trend values (see above equation). Size and complex properties of b are set automatically. |
|
[In] TVec L |
Seasonal indices (see above equation). Size and complex properties of L are set automatically. |
|
ref double Alpha |
Defines initial estimate for Alpha, returns Alpha which minimizes MSE. |
|
ref double Beta |
Defines initial estimate for Beta, returns Beta which minimizes MSE. |
|
ref double Gamma |
Defines initial estimate for Gamma, returns Gamma which minimizes MSE. |
|
[In] int Period |
Period length. An exception is raised if Y.Length mod Period is not 0. |
MSE, evaluated at minimum.
Performs triple exponential smoothing (also known as Holt-Winters smoothing) using the following equations:
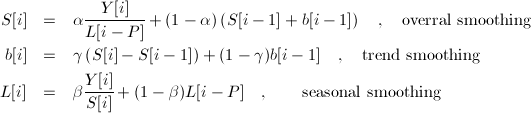
where Y are the observations, S are the smoothed observations, b trend factors, L the seasonal indices and P is the period length. To initialize triple exponential smoothing method we need at least one complete season's data to determine initial estimates of the seasonal indices L[0]..L[P-1]. Again, there are several ways to initialize L values. The algorithm uses approach, described at www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/pmc/section4/pmc435.htmpage. For initial estimate for S and b, the following equations are being used:
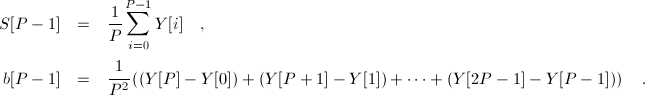
Note There are no S[0]..S[P-2] values; the smoothed series starts with the smoothed version of the Y[P] observation. Also note that the internal algorithm automatically accounts for this by resizing S,b vector to Y.Length-Period.
Generate 24 random values representing 4 quarters x 6 years = 24, perform smoothing and read Alpha,Beta,Gamma + MSE.
|
Copyright (c) 1999-2024 by Dew Research. All rights reserved.
|
|
What do you think about this topic? Send feedback!
|